This topic takes on average 75 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Biology
Biology
Every cell contains high levels of inorganic phosphate ions (-PO43-). Sometimes one of the fatty acids in a triglyceride is replaced by a phosphate group to form a phospholipid. Phospholipid molecules have a hydrophilic region around the phosphate group which is soluble in water and hydrophobic regions around the fatty acids which are not soluble and repel water. This is a key element in the structure of cell membranes and so in the nature of life itself.
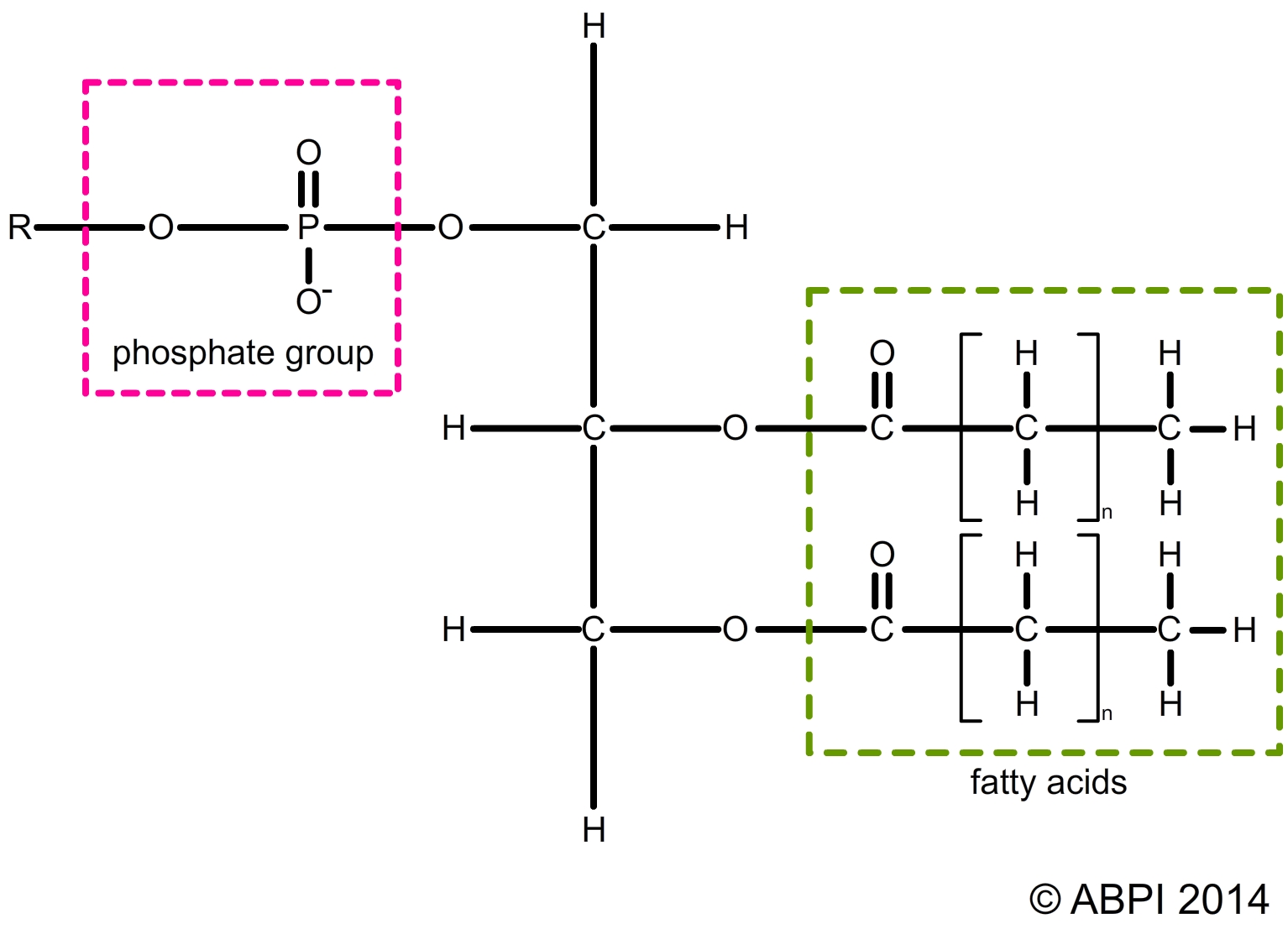
Structure of a phospholipid – the hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions of the molecule have a major effect on the structure of cell membranes
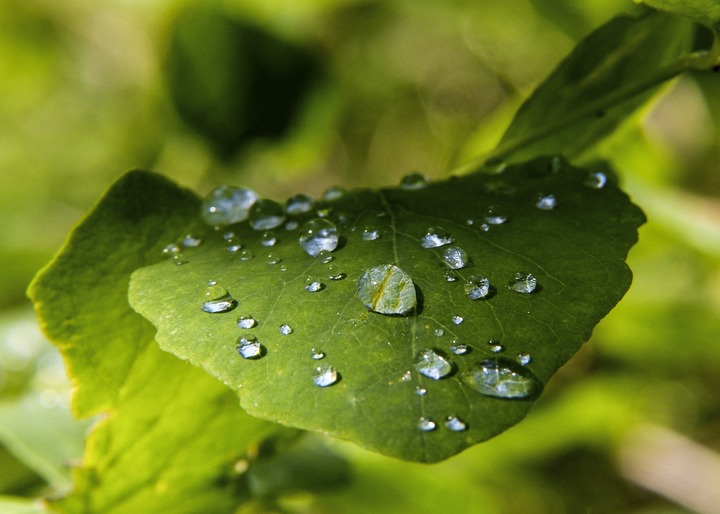

Waxes are lipids made up of very long chain fatty acids joined to alcohols by ester bonds that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic polar solvents. The big difference between waxes and triglycerides is that in waxes there is only one fatty acid joined to a single alcohol, because alcohols only have one available hydroxyl group, unlike glycerol which had three. Waxes on the surface of leaves and insect cuticles, along with oils on feathers and fur, form a water-proof layer which enables the organisms to survive in their environments.
Steroids are insoluble in water but otherwise are not typical lipids – they are made up of large numbers of carbon atoms arranged in complex ring structures. They are very important in biological systems as hormones.
Other lipids or lipid-derived molecules which are important in biological systems include:

For years the scientific evidence suggested saturated fats in the diet increased the risk of coronary heart disease. More recently, scientists have thrown doubt on this.
Investigate this using a variety of sources (for example the internet, scientific journals or interviews with experts if you can). Then write two articles in different styles:
