This topic takes on average 75 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Biology
Biology
Polysaccharides are giant polymers of monosaccharides, all connected by glycosidic linkages. They have an enormous range of functions in different organisms (see above). They may have a relatively simple structure or they may form more complex molecules, depending on the monosaccharide units and the types of glycosidic bonds involved.

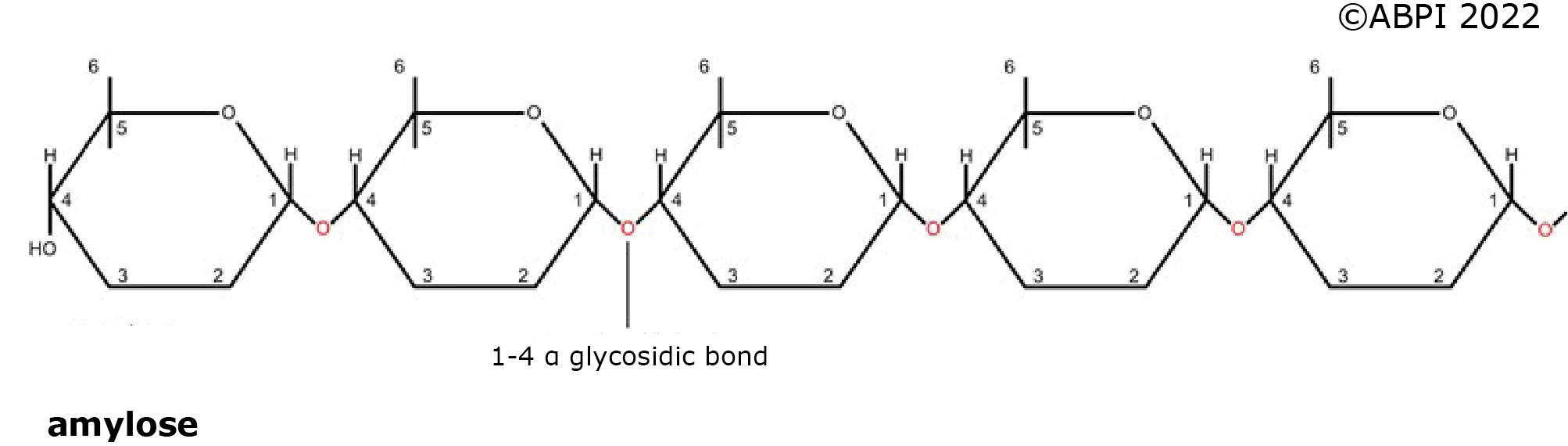
1. Amylose - an unbranched polymer made in plants made up of 200 - 5000 glucose units all joined by α-1,4 glycosidic bonds. It forms spiral molecules, so it is very compact – ideal as a storage molecule.
2. Amylopectin - a plant polymer made up of glucose units joined mainly by α-1,4 links but with some α-1,6 linkages, so the chains branch around every 24-30 glucose units. It is not as compact as amylose, but as all the chain ends are available for enzymes to hydrolyse the bonds, it can be broken down quickly to provide glucose for cellular respiration.
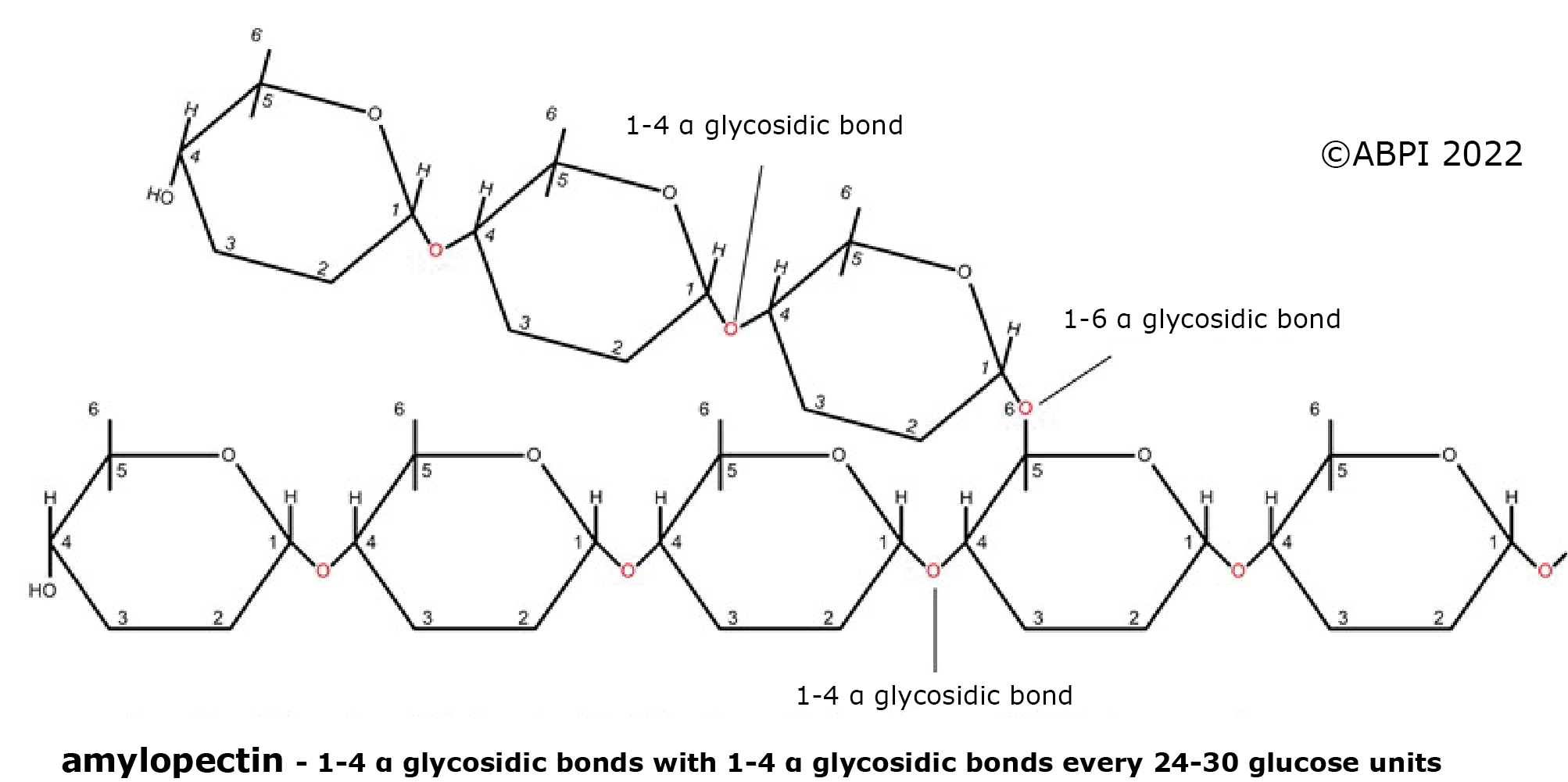
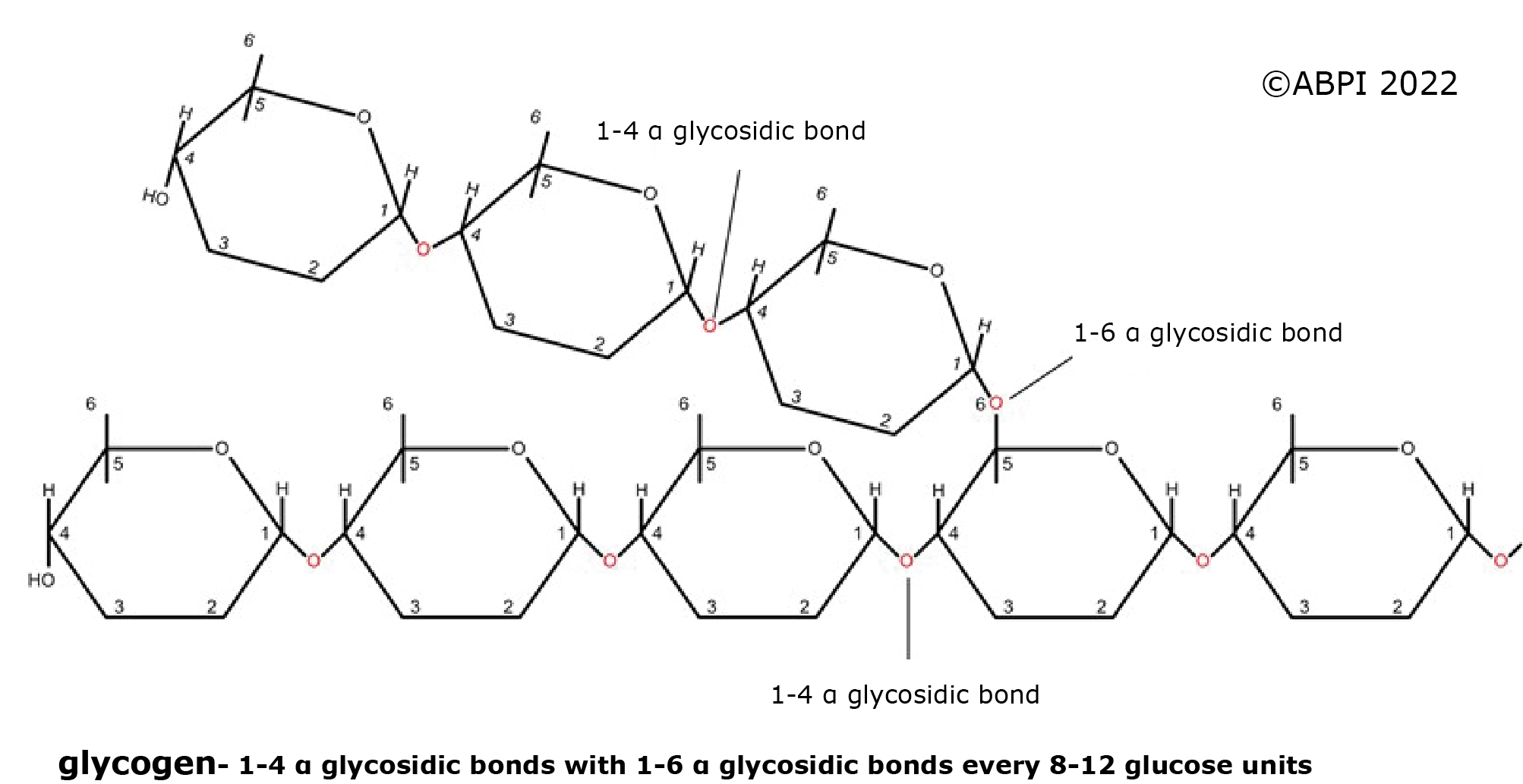
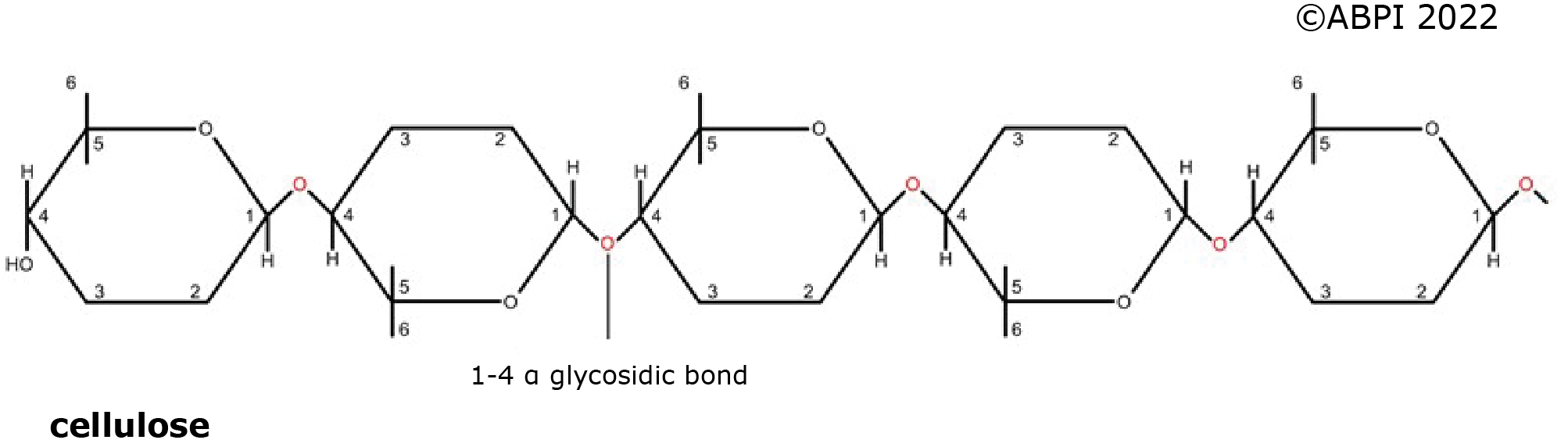
The nature of these polysaccharides depends on the isomers of glucose involved in the molecules, and the type of glycosidic bonds formed.
You can find examples of infographics and data visualisation at the links below:
www.informationisbeautiful.net
www.theguardian.com/membership/2014/sep/10/best-infographic-graphic-design
