This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
Genetic information is stored in DNA, which is found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. The complete amount of genetic information present in an organism is called the genome. Understanding the human genome can be seen as the key to understanding the mystery of human life itself. Read more about the Human Genome Project.
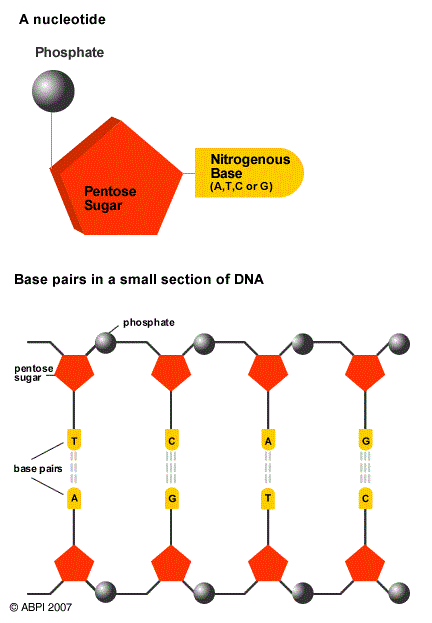
Most cells in the human body have a nucleus containing 23 pairs of chromosomes. Chromosomes are made from very long molecules of DNA. Each molecule is in a ladder-like shape, with the ‘rungs’ being made from a pair of nitrogenous bases, known as A, T, G or C, and the sides made from repeated pentose sugars and phosphate groups. A group of one base, one pentose molecule and one phosphate together is known as a nucleotide and DNA can be regarded as a polymer of these nucleotides.
The bases are always paired A with T and G with C and it is the exact sequence of these base pairs in the DNA molecule that maps out the genetic code of the individual.
The DNA molecule is twisted into a double helix and coiled so tightly, that the total length of the human genome, about 1.8m, fits inside a nucleus of diameter about 6μm.
A small section of a chromosome that controls particular characteristics, is called a gene. Each chromosome carries hundreds of genes; scientists have identified 20,000-25,000 human genes. Only some of the full set of genes is used in any one cell – some genes are ‘switched off’.
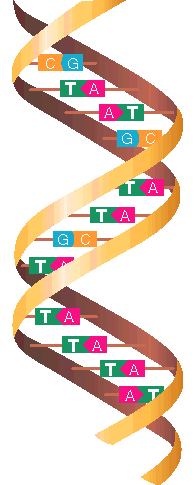
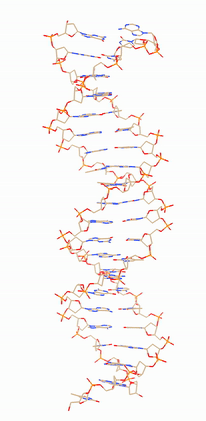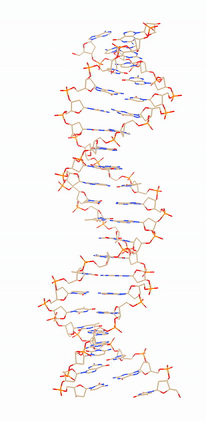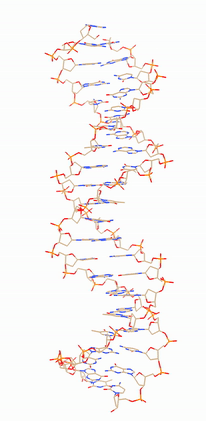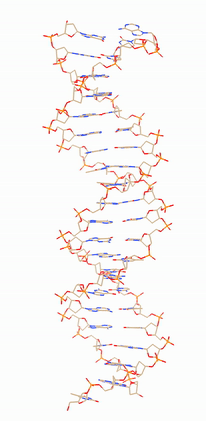
The chromosomes in a pair carry the same genes at the same positions. One of each pair has come from a different biological parent, so the genes are also in pairs and both code for the same characteristic. These alternative forms of one gene are called alleles or variants.
An individual may have two alleles the same or two different alleles for any one gene. Individuals carrying two of the same alleles are known as homozygous, whereas those carrying two different alleles are heterozygous. When alleles are different, it may be that one of the alleles is dominant and the other recessive. A dominant allele always shows its related characteristic in the individual.
A gene is a piece of DNA which has the code for a particular protein. The order of the bases in the gene determines the order in which amino acids are put together to make the protein. Proteins have special functions in the body, so it is very important that the correct proteins are made.