This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
Meiosis is the process by which new cells with half the usual number of chromosomes are produced. In humans the full complement of 46 chromosomes is called the diploid number. Meiosis produces cells with 23 chromosomes, known as the haploid number, and these are the gametes, i.e. sperms for males and ova for females.
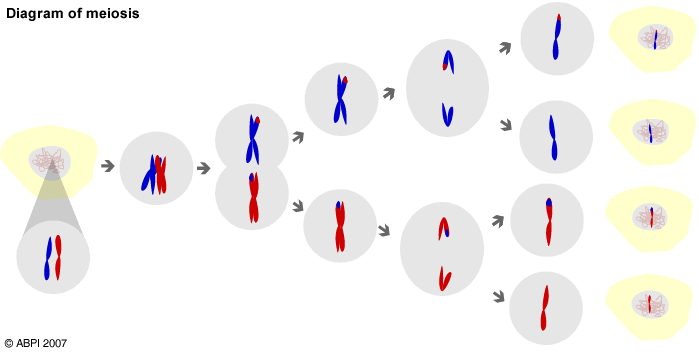
In meiosis there are two lots of cell division so that a single diploid cell gives rise to four haploid cells. During fertilisation two haploid nuclei join to give a zygote with the diploid number of chromosomes. The zygote then grows and develops by mitosis.
Many characteristics are controlled by a gene (or sometimes a few genes). The gender of the next generation, however, is determined by a whole chromosome. Human chromosome pair number 23 differs between male and female. It can be XX, which is female, or XY, which is male. In the following genetic diagram, the letters represent chromosomes.
It shows that the ratio of boys to girls is 1:1, that is, there is always an equal chance of getting a boy and a girl.