This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
Living organisms are made up of cells. Understanding the structures and functions of cells is the key to understanding how whole organisms work and interact with the world around them.
How does your body recognise an invading pathogen? How do cells communicate so they can act as a coordinated whole? Why are transplanted organs rejected without immunosuppressant drugs? What are the differences between your cells and those of bacteria?
The size and structure of cells varies enormously, but there are many common features. The cell surface membrane forms a barrier between the contents of the cell and the environment. Membranes also surround all the organelles inside the cell. The structure of these membranes affects the functioning of almost every aspect of the cell.
Cells act as biological factories, producing many different substances which need to be exported to different regions of the cell or the body. Often these substances are produced as a result of signals from inside or outside the cell itself.
Cells display complex identification systems on their surfaces, and these act as part of overall cell communication. These systems are sometimes used by pathogens to gain entry to cells – and both surface identification systems and internal communication cascades can be used as targets for drugs in the battle against disease.
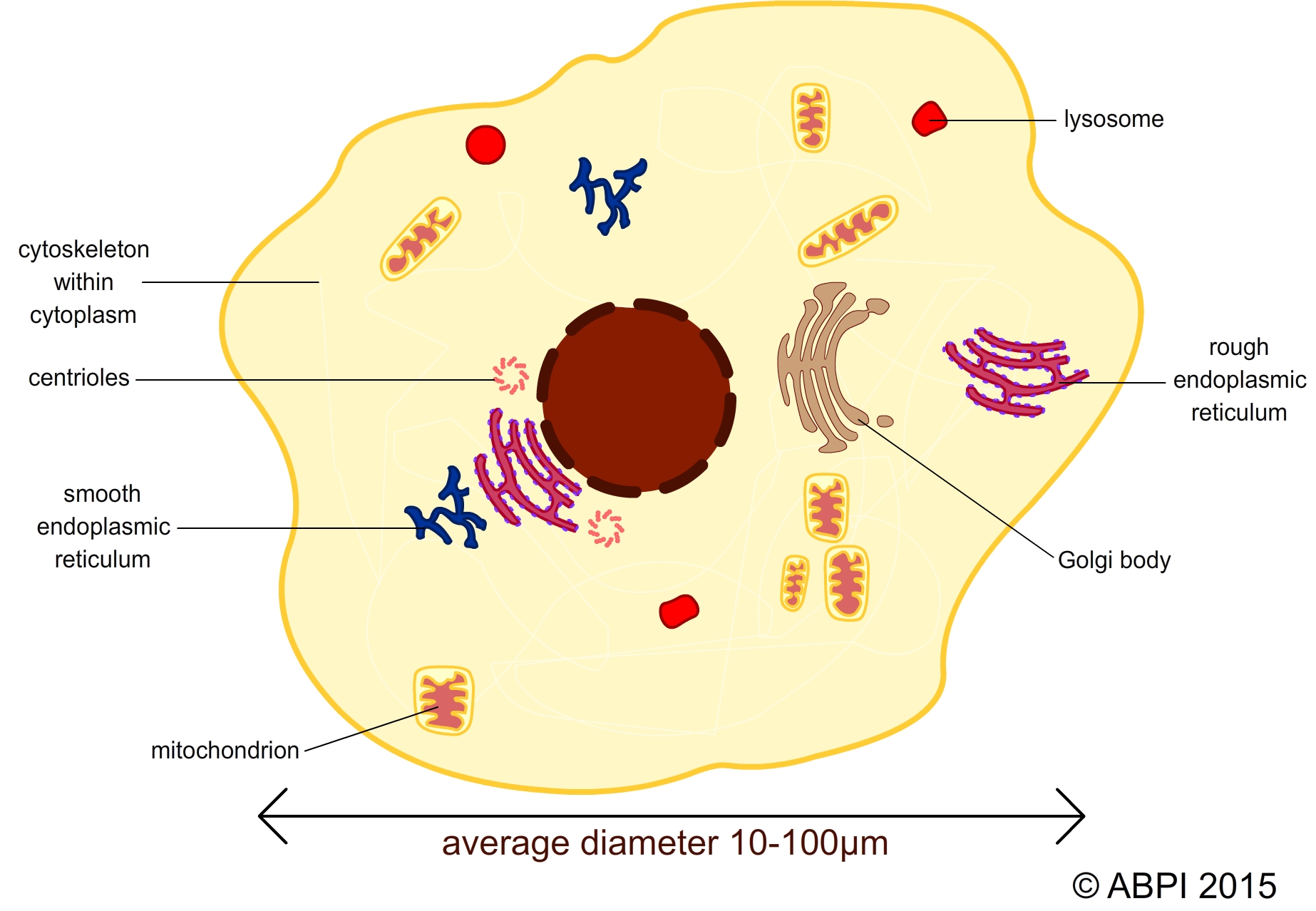
A cell contains a hundred or more chemical reactions, each contained by membranes and controlled by enzymes. This diagram depicts a eukaryotic animal cell.