This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
Vaccines are not the only form of medical treatment which relies on the immune system.
Monoclonal antibodies are antibodies which are made to target particular cells or chemicals in the body. Some lymphocytes (called B lymphocytes) make antibodies but cannot divide. Scientists combine mouse B lymphocytes which have been stimulated to make a particular antibody with a type of tumour cell to make a cell called a hybridoma.
Hybridoma cells can both make a specific antibody and divide. The hybridoma cells are cloned to make a large number of identical cells which all make the same antibodies. The antibodies are collected and purified. These are monoclonal antibodies - antibodies from a single clone of cells
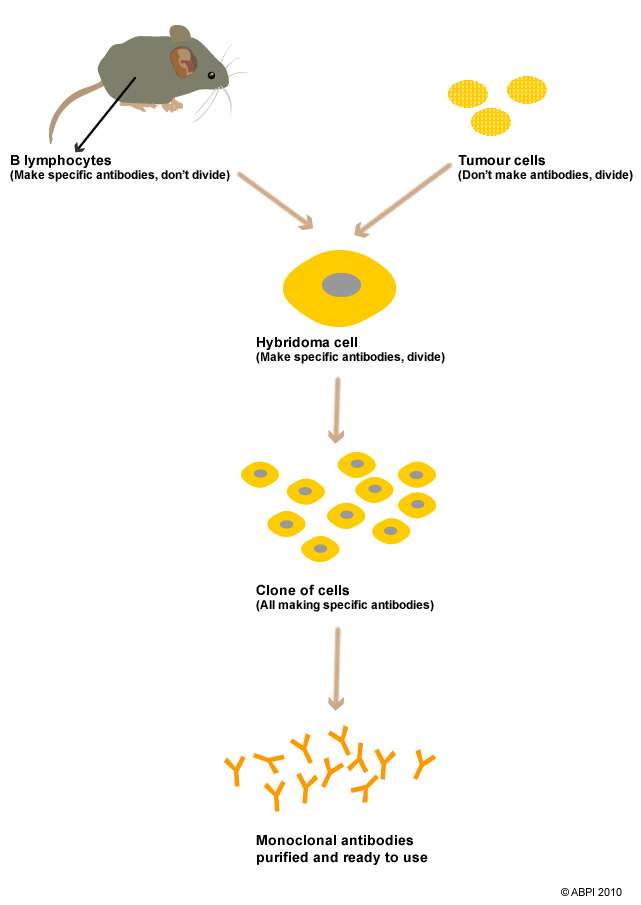
Making monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies produced by hybridoma cells can be used in a number of ways
A positive pregnancy test - they are so sensitive that they can be taken on the first day of a missed period.
© iStock photo.com
The potential advantages of using monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of cancer are great because monoclonal antibodies only bind to the specific cancer cells that need treatment. Healthy cells are not affected at all. In contrast conventional drug treatment is carried all around the body in the blood and can have a devastating effect on healthy cells as well as cancer cells. Radiotherapy treatment is targeted on the area of the body affected by the cancer but still usually affects the healthy tissue in the area as well.
However monoclonal antibodies create more side effects than expected. Doctors and scientists thought they would act like a 'magic bullet' affecting only the diseased tissue. It hasn't quite worked out like that and monoclonal antibodies are not yet as widely used or as successful as everyone hoped.