This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
 Human biology
Human biology
 Physical education
Physical education
Sometimes the kidneys become inflamed. This is called nephritis. It may be because the kidneys have become infected by bacteria - if so, it can be treated by antibiotics.
Kidney stones are hard mineral deposits formed in the kidney. They can pass into the urine and larger ones may stick in the ureter. Kidney stones can be very painful.
The stones can be smashed into smaller pieces using ultrasound. Then the pieces are passed out of the body in the urine.
This is a genetic disease. Polycystic kidneys become covered in fluid filled cysts and may become very enlarged - they can weigh around 12kg! Eventually, in some people, they stop functioning altogether.
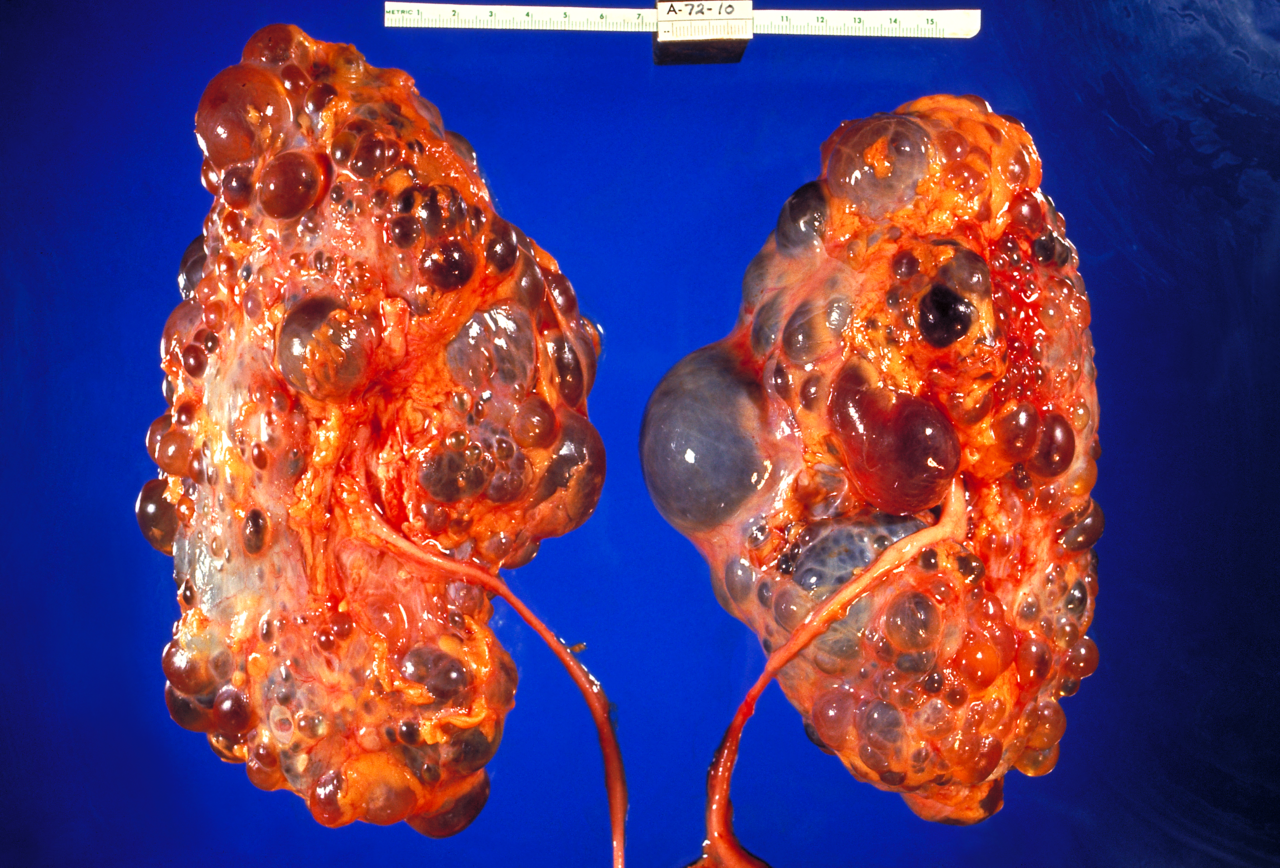
Polycystic kidneys can become huge but they do not balance and clean the blood efficiently (CDC, Dr Edwin P Ewing Jr)
Serious kidney disease may stop the kidneys working properly. When both kidneys stop working, this is kidney failure. Kidney failure can also be caused by injury, high blood pressure, poisoning or dehydration.
If the kidneys don't work, waste products build up in the bloodstream and the person will die without treatment. Treatment must replace the functions of the kidneys to remove waste and balance the water and salt levels of the blood. At the moment there are two types of treatment which can replace these kidney functions - either dialysis or a transplant.
Healthy kidneys also produce erythropoietin, a hormone that controls how fast new red blood cells are made. People with kidney failure don't make enough erythropoietin. As a result, they become anaemic because they can't produce enough red blood cells (red blood cells only last around 120 days). Patients can take synthetically produced erythropoietin (EPO) to ensure enough red blood cells are made.