This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
 Human biology
Human biology
 Physical education
Physical education
Substances are moving in and out of the cells of your body all the time. To understand why the water balance is so important in homeostasis, and to make sense of how your kidneys work, you need to know about diffusion, osmosis and active transport.
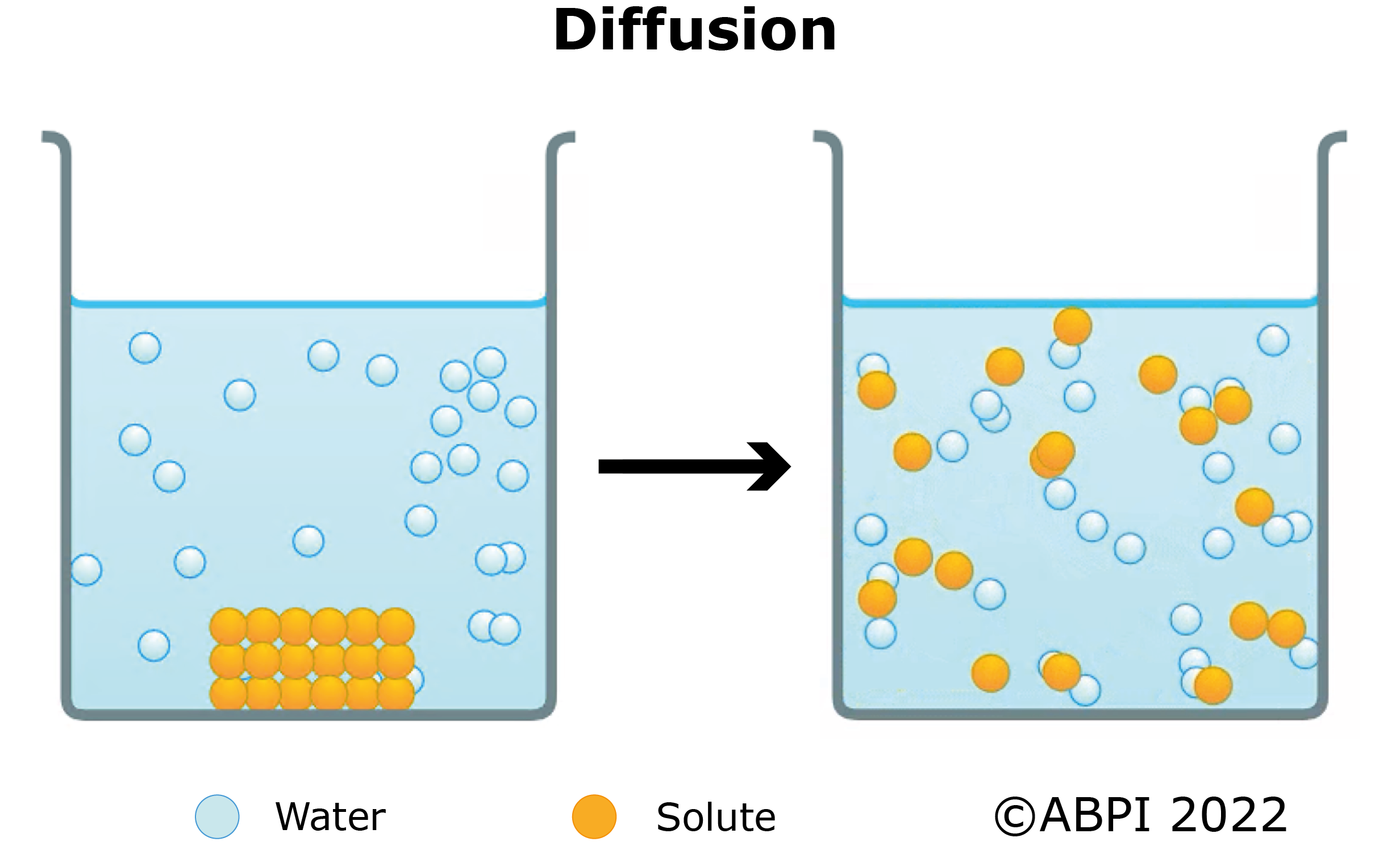
Diffusion is the spreading out of the particles of a gas or any substance in solution. It is caused by the random movement of the particles. The higher the temperature, the faster the particles move, and the faster diffusion takes place. Diffusion results in the overall (net) movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration down a concentration gradient. If there is a big concentration difference diffusion will take place more rapidly than if there is only a small concentration difference. The difference in concentration is known as the concentration gradient.
Diffusion is very important in the body for the movement of substances. For example, in the lungs, oxygen moves from the air to the blood. This movement is diffusion, as oxygen concentration is higher in air, than in the blood. Carbon dioxide also diffuses from the blood, where its concentration is higher, to the air in the lungs. Another common example would be the movement of glucose from the blood (higher concentration) to the cells (lower concentration).
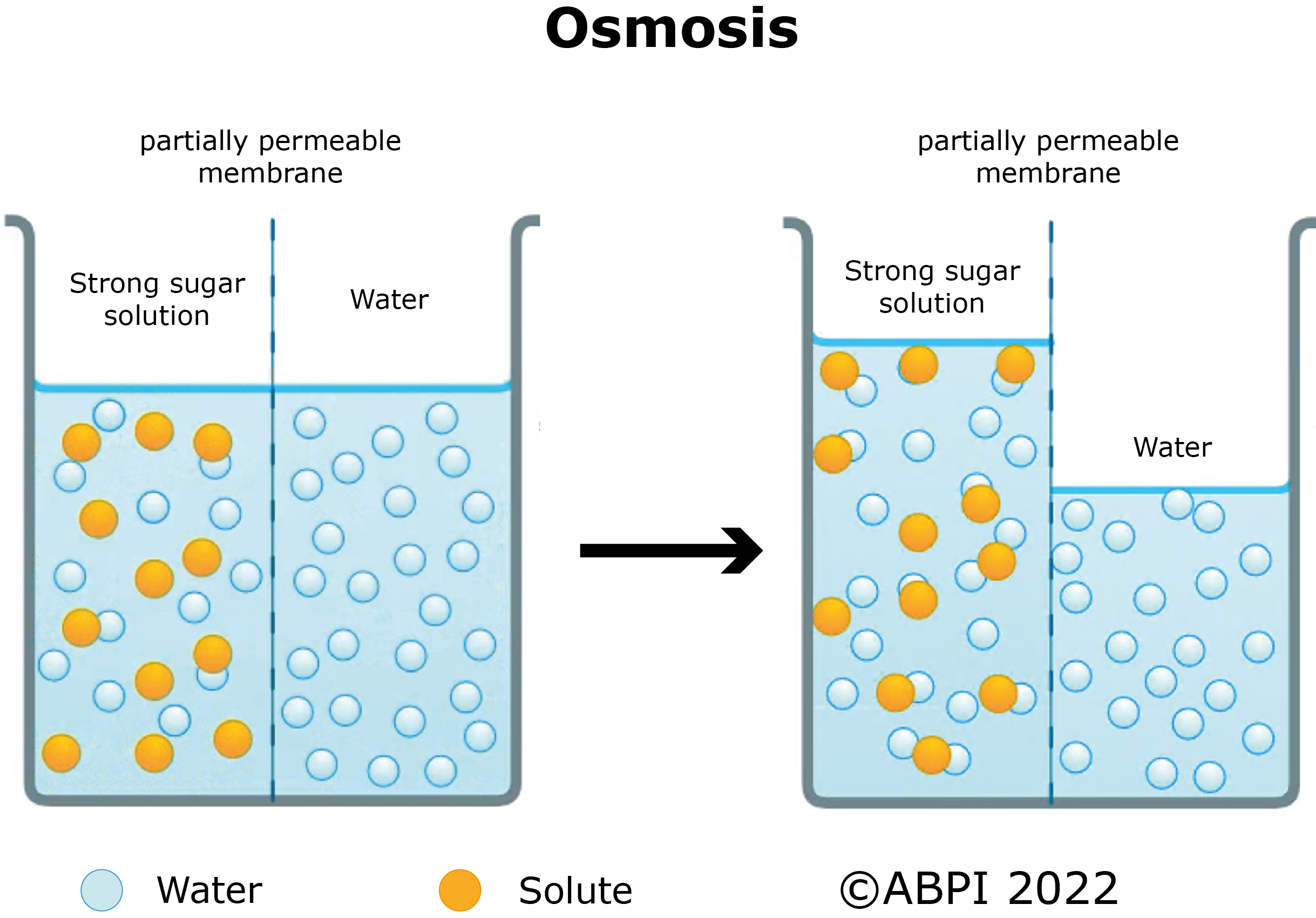
Osmosis takes place when two solutions are separated by a partially permeable membrane. A partially permeable membrane lets some particles through but not others. Cell membranes are partially permeable. Water can move freely through them but other particles, such as sugar molecules, cannot.
Osmosis is the movement of water through a partially permeable membrane down a concentration gradient from a dilute solution (where there is a lower solute concentration) to a concentrated solution (where there is a higher solute concentration).
The movement of water by osmosis is the main reason why it is so important to control the water balance of the body. Osmosis is vital for plants and is what allows them to draw water from the soil. Plants to this by concentrating solutes in root cells using active transport. Those cells have a higher solute concentration than the soil, and as a result, water flows from the soil to plant root cells.
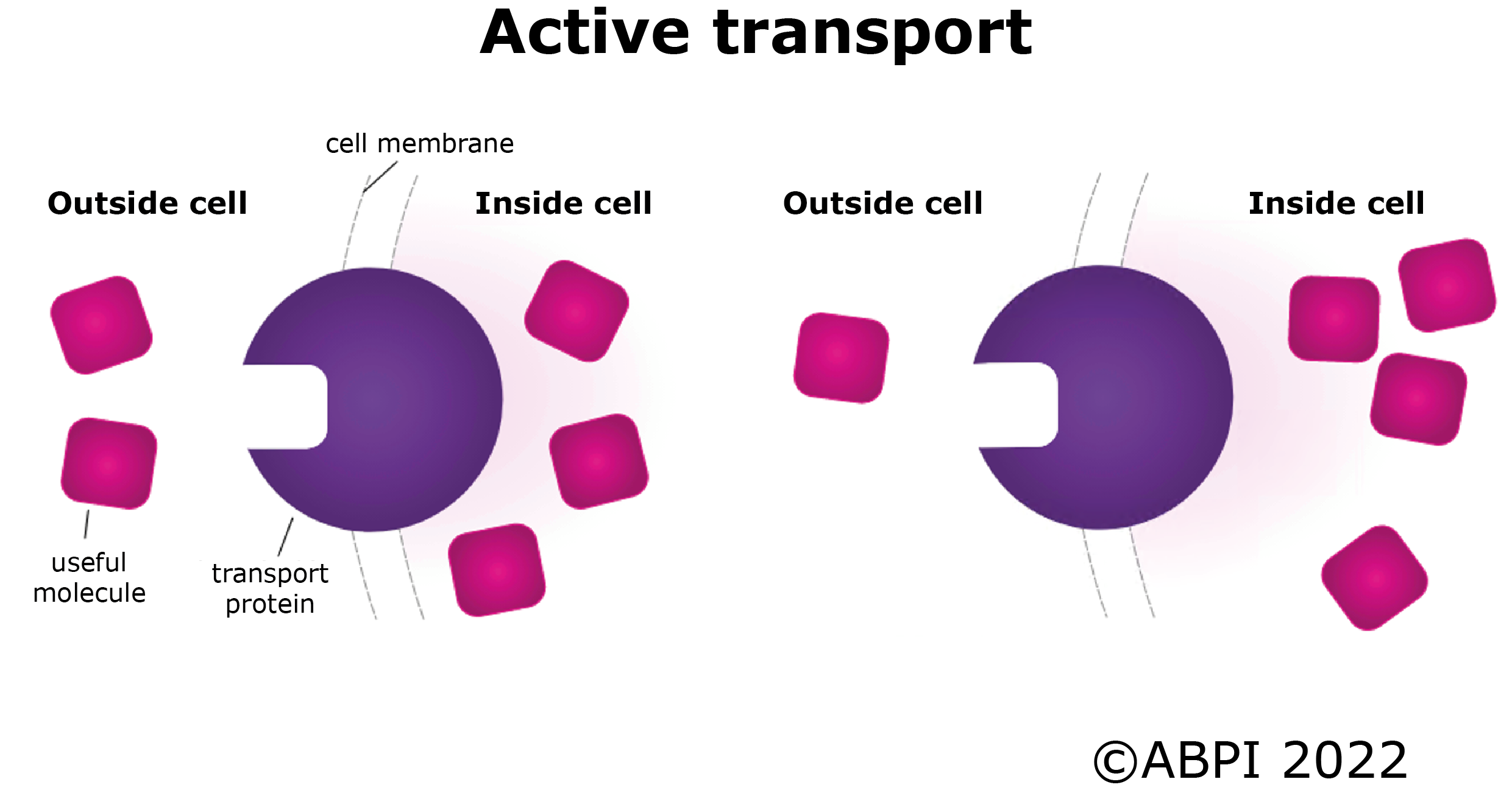
Active transport uses energy to move substances against (up) a concentration gradient or across a partially permeable membrane. In active transport a special transport protein in the cell membrane picks up the useful particle on one side of the membrane. The transport protein then rotates through the membrane and releases the particle on the other side of the membrane. This uses energy from cellular respiration.
Active transport is used to move substances into cells and out of cells. Cells which carry out a lot of active transport often have lots of mitochondria to give them the energy they need. Active transport is important in the kidney for hanging on to the substances needed by the body such as glucose and some sodium ions. Another example would be the movement of water from plant root cells to other plant cells. This is active transport, as there is not a difference in solute concentration, as when the water entered the root cells from the soil. Ions moving from soil into plant roots is another example of active transport.