This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
 Human biology
Human biology
 Physical education
Physical education
 Science
Science
Around a third of all the people in the UK will die of some form of cardiovascular disease - mainly heart attacks and strokes.
It makes good sense to try to reduce the risk of developing CVD. There are a number of simple steps which will help:
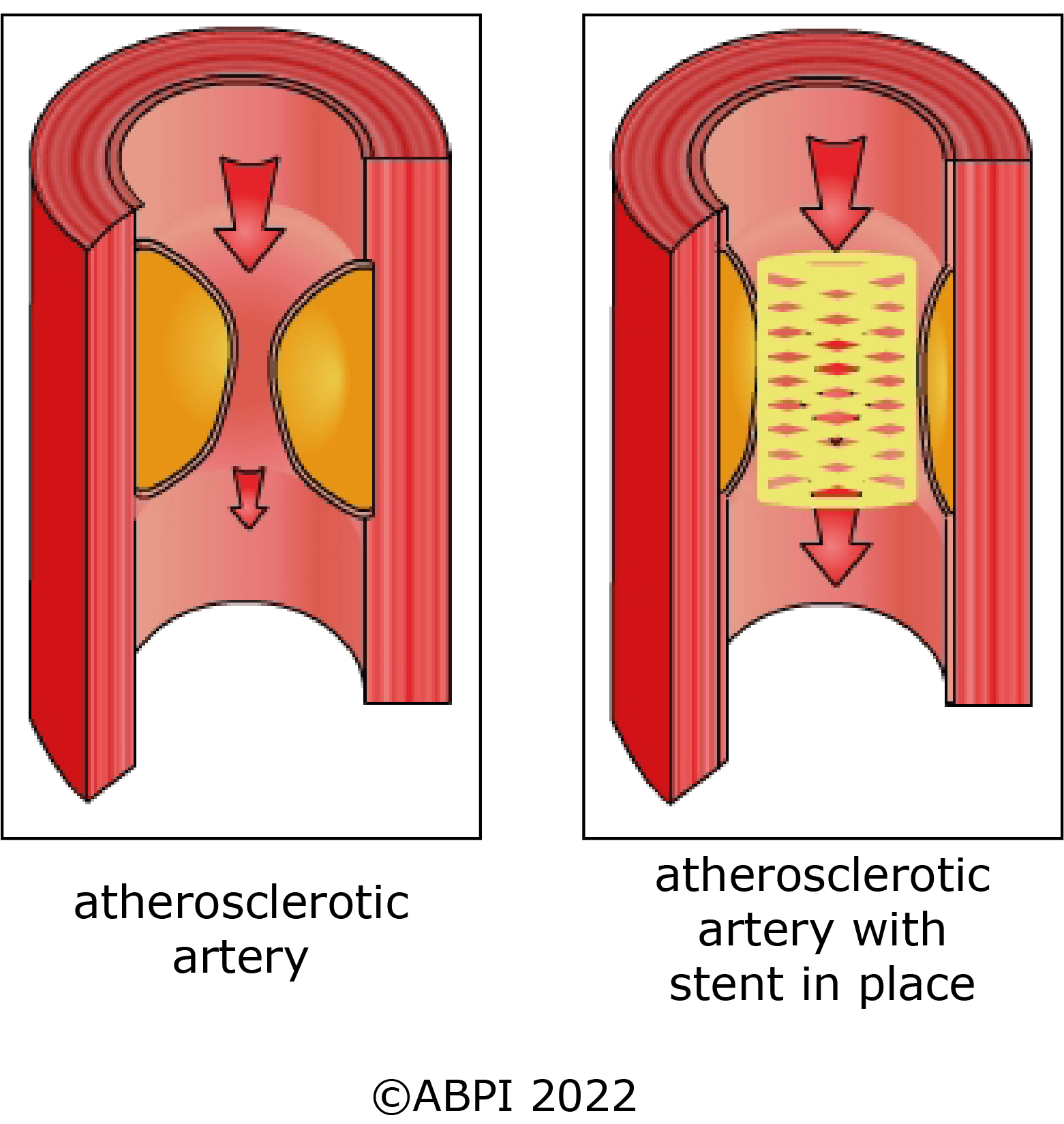
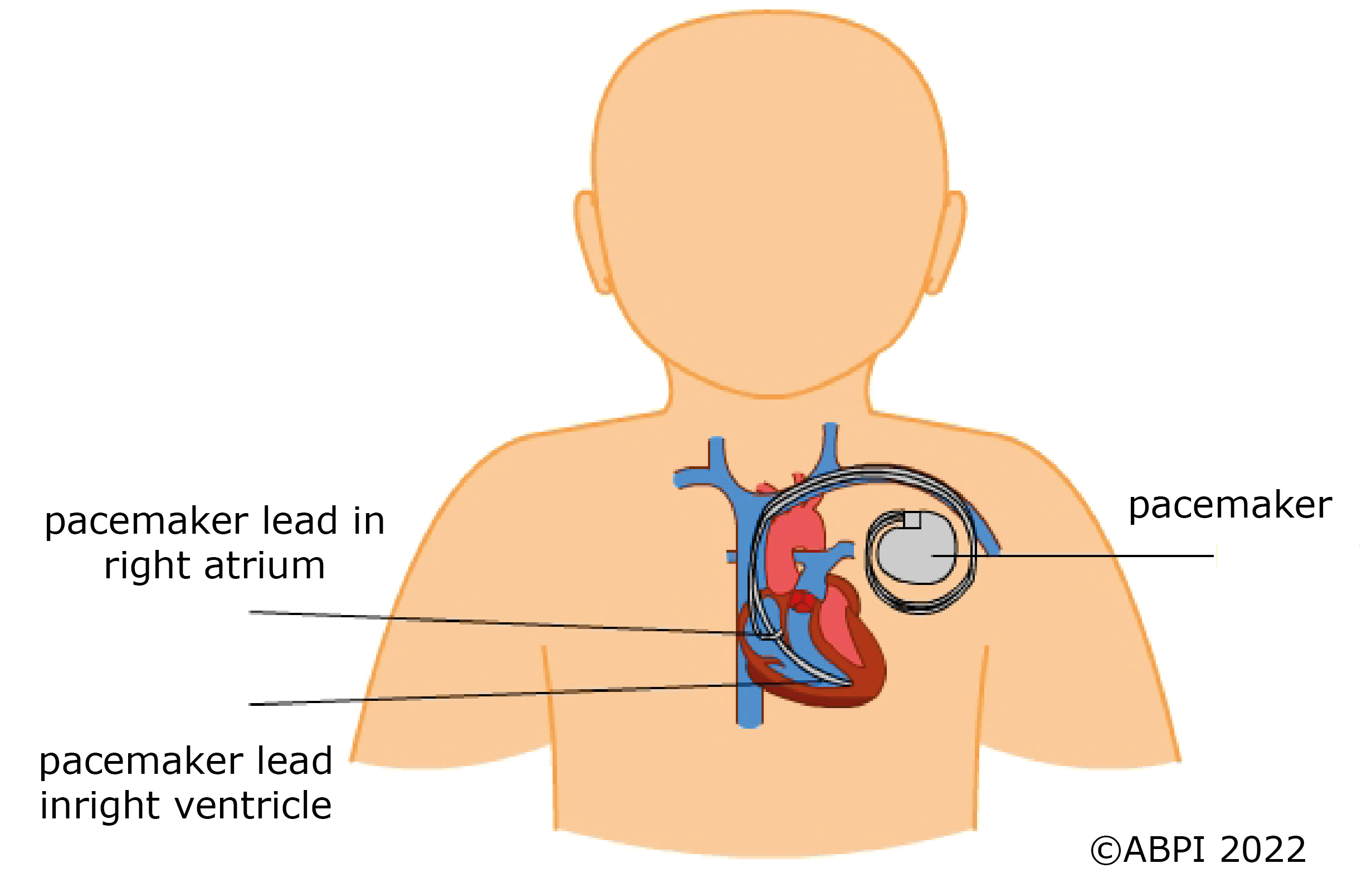
Many people make lifestyle choices which increase their risk of CVDs. But even with a healthy lifestyle, many people will still suffer from some form of CVD. Luckily there are many different treatments which doctors can use to both help prevent disease and to treat any problems which occur.
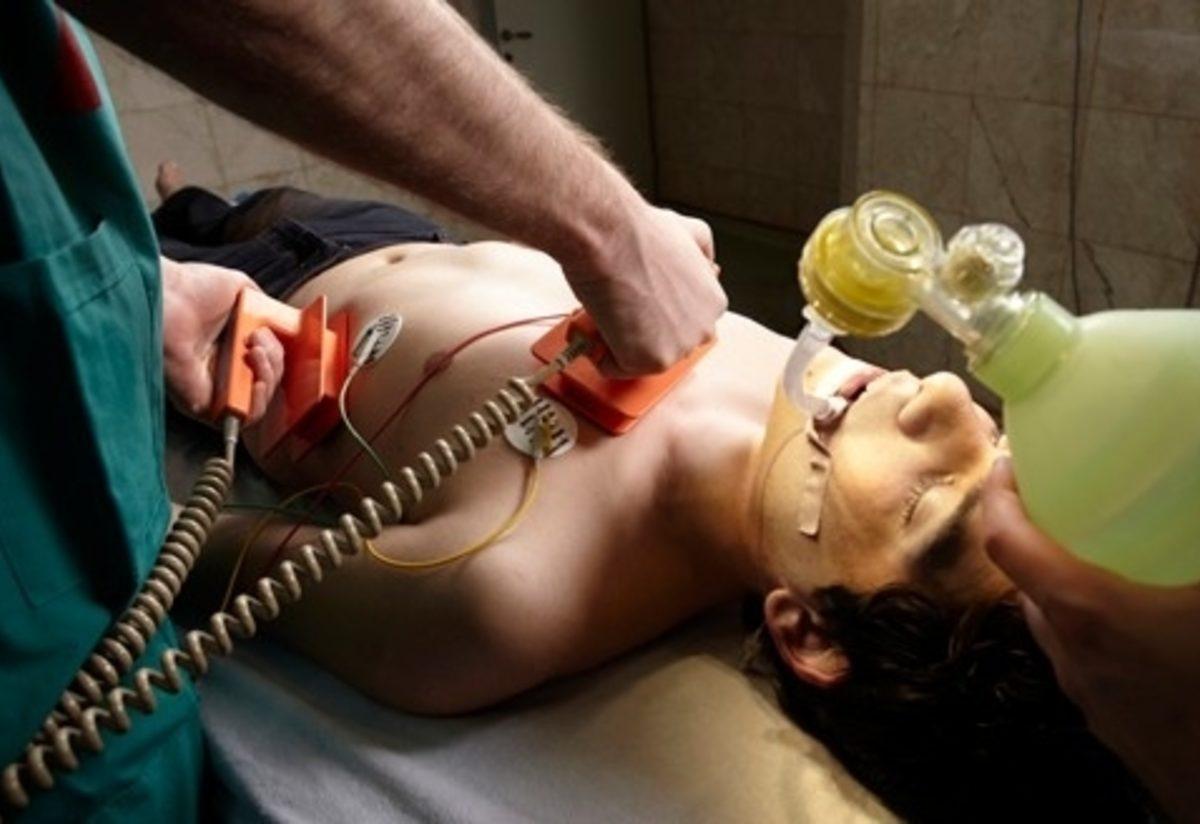
Defibrillators can save lives
If someone has a heart attack, doctors try to get them stable enough to have bypass surgery, stents or treatment with medicines to keep them alive and well.