This topic takes on average 120 minutes to read.
 Biology
Biology
 Science
Science
Communicable diseases are cause by pathogens, which are infectious. Pathogens include bacteria, fungi, protozoa and viruses, and they are transmitted between people or animals to allow the disease to be spread. This transmission can occur via direct contact, by water or by air.
Bacteria:
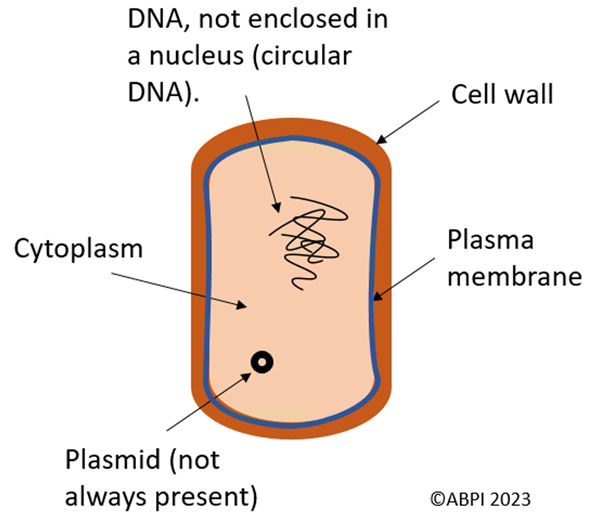
Viruses:
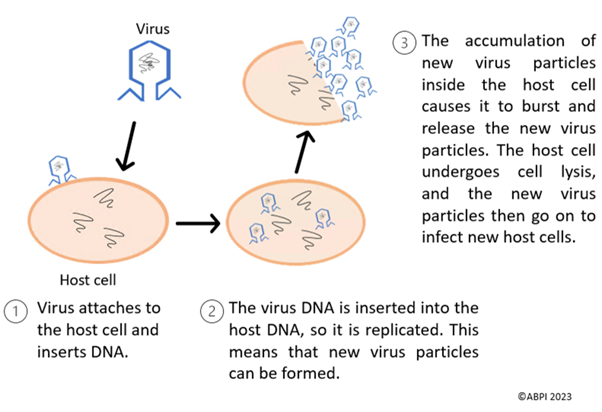
When the body is infected with a communicable disease, it fights back via the immune system to fight off the infection. Modern medicine has also developed many successful treatments to assist the body’s natural defences, including antibiotics.
You can find more detailed information about pathogens in the pathogens resource, and more information on specific infectious diseases that they can cause in the diseases resource.