This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
 Human biology
Human biology
 Science
Science
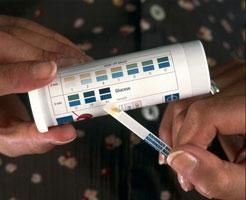
The simplest way to detect diabetes is to look for glucose in the urine. A glucose test stick changes colour to indicate the level of glucose.
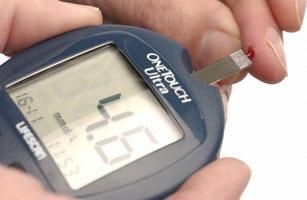
People with diabetes regularly monitor their blood glucose level by using a digital monitor. A drop of blood is placed on a test strip and the monitor displays the blood glucose concentration.
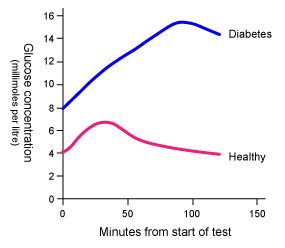
To confirm diabetes, a person will normally take a glucose tolerance test in a hospital.
Patients do not eat for 12 hours before the test. This gets their blood glucose to its lowest level. They are then given a drink containing 75g of glucose and their blood glucose level is monitored over the next two hours.
Every cell in the body needs a supply of glucose to maintain respiration and generate energy for all of its processes. Levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood are closely controlled by two hormones; insulin and glucagon.
Use the animation to see how the body responds to high and low blood sugar levels: