This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Human biology
Human biology
 Biology
Biology
 Physical education
Physical education
Cellular respiration takes place in all of the cells of your body, providing the energy they need. The breathing system moves air in and out of your body, delivering the oxygen needed by the cells for respiration and removing waste carbon dioxide. In conditions such as asthma, the breathing system cannot work efficiently and scientists and doctors have to find ways to enable sufferers to breathe easily again.
From the moment you are born until the time when you die, you will breathe air in and out of your body. Why is breathing so important for life? The cells of your body need a constant supply of oxygen for cellular respiration to provide the energy needed for all of the reactions of the body. Poisonous carbon dioxide is a waste product of these reactions and it needs to be removed.
The breathing system is contained in the chest. Air is breathed into the lungs. Oxygen from the air moves into the red blood cells and carbon dioxide from the blood moves into the air by diffusion. This process is known as gaseous exchange.
The muscles between the ribs and the muscular diaphragm bring about changes in the volume of the chest which move the air in and out of the lungs.
Asthma is a common condition which affects the airways and makes it difficult to move air in and out of the lungs. Other diseases of the lungs also affect gaseous exchange. Sometimes our own behaviour contributes to problems with the breathing system – for example smoking is known to increase the risk of many respiratory conditions. Different medicines enable doctors to cure or control many diseases of the breathing system.
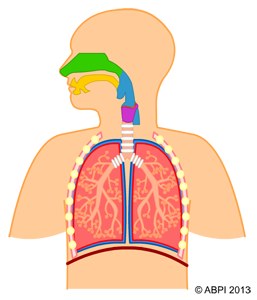
The breathing system